(Plain Text Version)
Let’s continue our tour of summer showpieces with three objects close to the bright white star Vega:
The Ring Nebula
For most of its life, a star produces energy by combining hydrogen atoms in a fusion reaction. When the hydrogen is consumed, some sort of transition will take place. In this case, the outer layers of the star’s atmosphere have expanded and escaped. From our point of view, this gas appears as a ring. The core of the star shrank into a bright, super dense form called a white dwarf. Intense radiation from the white dwarf illuminates the gaseous ring.
Although the Ring Nebula is visible with a small telescope, bigger scopes reveal many colorful details.
The Double Double
Through a small telescope, the Double Double appears as two rather brilliant stars. These “stars” orbit each other. When viewed with a medium-sized telescope, the two “stars” are found to be two pairs of stars. The stars in each pair orbit each other. Hence the name “Double Double”: a pair of double stars.
T Lyrae
T Lyrae is a carbon star, a red giant star with an atmosphere rich in carbon. It has a vivid red-orange color due to the carbon compounds in its atmosphere. The red giant phase occurs after a star’s hydrogen has fused into helium. This happens late in the life cycle of the star.
Carbon stars are beautiful because their color contrasts with the neighboring stars. More importantly, the carbon is eventually expelled from the star and travels to other places. Much of the life-sustaining carbon on Earth came from ancient Carbon Stars.
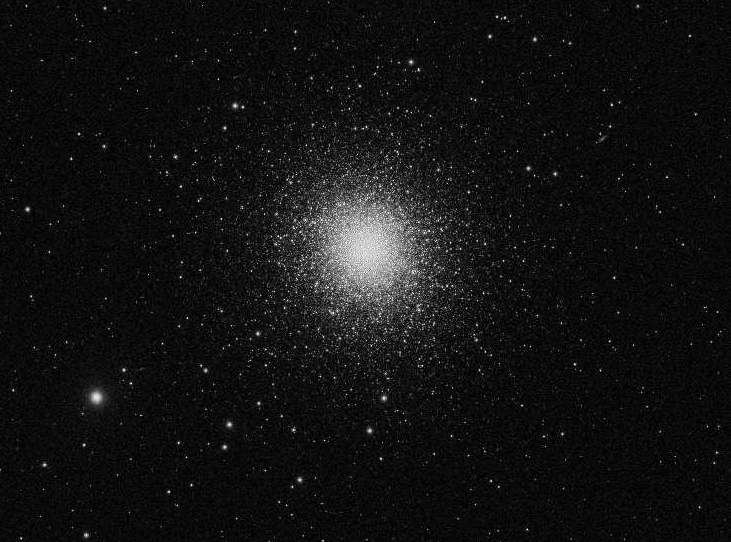
The Hercules Cluster
Not too far from Vega and the Summer Triangle we find the Hercules Cluster. This is a globular cluster, a group of several hundred thousand stars which orbit a common point. These orbital paths are stable and continue for a long time.
If one lived on a planet inside a globular cluster, the night sky would always be bright. The view would be dominated by the stars of the cluster. When viewing through a telescope, it would not be obvious which objects are members of the cluster and which ones are farther away.
With a small telescope, the Hercules Cluster appears to be a small fuzzy blob. With bigger instruments, many individual stars can be seen.